Digital Application Services

Our Digital Applications Services
An individual can utilise up to 20 enterprise-office programmes each day in a normal corporate workplace, while the average end-user checks their phone 64 times per day.
This, combined with the current business cliché that “all organisations are tech companies or will become tech firms or perish,” highlights the importance of speeding up the development of contemporary digital applications for all stakeholders, including customers, employees, partners, and affiliates.
When it comes to attracting and retaining top people in the future, outdated and archaic corporate software will quickly become a burden. The enormous disparity between the quality of customer-facing digital experiences and the quality of business applications is narrowing.
Companies who close the gap as soon as possible will receive the full benefits.
From banking and transportation to healthcare and even the way we use technology in workplaces, more and more tasks are going digital. Applications are the main driving force behind these engines of change. Applications have become the focal point of businesses as a whole – ensuring product and service quality, enhancing operational efficiency and boosting profits are all dependent on an organizations ability to innovate its application estate. Enabling application-centric transformation has become crucial for building a digital future.
From banking and transportation to healthcare and even how we utilise technology in the workplace, more and more services are becoming digital. Applications are the primary driving factor behind these change engines. Every organisation now revolves around its applications; the ability of a corporation to reinvent its application estate determines product and service quality, operational efficiency, and revenue growth. It is vital to allow application-centric change in order to establish a digital future.
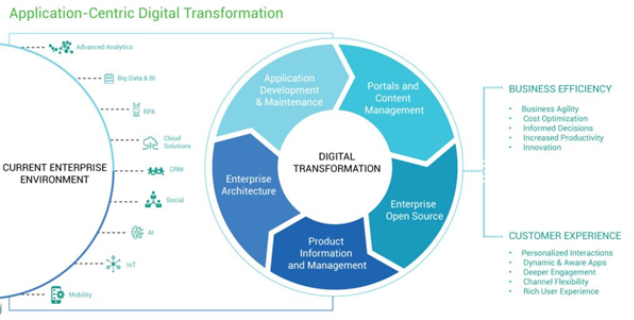
Digital Enabled Application Services aim to empower organizations across the entire application life cycle. From design to building and managing the applications, our application services experts work with our clients to facilitate application-centric transformation.
Redesigning enterprise architecture can help you generate more digital capital faster.
Transform your approach to business content management to deliver highly personalised experiences.
Improve omnichannel capability by implementing cutting-edge technologies.
Make your own apps to solve specific business concerns.
Manage high-volume inventories while maintaining accurate and up-to-date product information.
Develop new, dependable, resilient, scalable, and cost-effective apps faster with open source technology.
Using cohesive and forward-thinking techniques, our worldwide professional team produces customised digital enabled application roadmaps with vast industry experience. We help businesses define and convert goal architectural options to increase agility and profitability.
Tools deployed for Digital Applications Services
Digital enablers for the hybridisation of the physical and digital world
Sensors and embedded systems
Physical-digital hybridisation facilitators connect the physical and digital worlds by collecting data from the physical world or transforming digital data into a tangible form. Sensor technology, for example, can be utilised to improve a manufacturing process’ efficiency or functionality, resulting in process improvement.
Cybersecurity
Sensors, wearables, and other devices, as well as management software, must make data available to each other. To accomplish this, it must be transferred via the internet in a secure manner.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing allows enterprises to employ Internet computing capabilities for storage and large-scale data processing without having to invest in their own IT infrastructure, providing flexibility and scalability.
Connectivity and mobility
In today’s globalised society, information can be absorbed by a variety of devices and people from all over the world at any time. As a result, information must not only be transported but also processed, needing increased storage and processing capacity.
Intelligence and control solutions
Big Data is particularly significant in this market because it enables huge volumes of data to be gathered and advanced data analysis to be performed in real time, providing critical information for decision-making, process optimization, and increased business intelligence. All of this is made possible by data integration and visualisation platforms, which allow users to monitor, control, and administer their systems while also providing predictive insights to aid decision-making.
Business solutions
The usage of apps or business management systems, which encompass manufacturing processes, sales, accounting, supply, and so on, is one approach to track visibility on the actions that are carried out in the business strategy as well as the management of customers. Despite the fact that business management systems are not a new addition to the corporate landscape, they are becoming increasingly important, and it is vital to adapt them so that they can integrate data from devices and networks in a flexible and dynamic manner.
Advanced robotics
Robots are already a part of our everyday lives, both at home and at work, where they assist in the efficient and automated completion of tasks. Advanced robotics takes things a step further by allowing robots and control systems to communicate.
Capabilities Of Digital Applications Services
DIGITAL ENGAGEMENT
The way firms and business services activities interact with customers, suppliers, partners, and other stakeholders has been revolutionised by a flood of technological advancements, and the field is currently rapidly expanding. By digitising and integrating interactions across channels and exploiting data, these technologies can improve stakeholder experience.
DIGITAL SERVICE OPTIMIZATION
Due to the fundamentally dynamic nature of business processes and operating models, as well as the incapacity of business applications to adapt to changes at the speed at which company operates, business process automation has never fully delivered on its promise. The agility gap would increase even more unless technical platforms are redesigned and IT organisation capabilities are improved. To improve the efficiency and effectiveness of business services and the execution of underlying processes, digital service capabilities include content and process digitization, business process management, automated workflows and approvals, robotic process and cognitive automation, and robotic process and cognitive automation.
DIGITAL ECOSYSTEM
Traditional organisational structures and value chains are giving way to digitally connected networks of resources, service providers, and customers. Emerging digital ecosystems include business-to-business networks, knowledge networks, and the internet of things (IoT). Companies can use a knowledge network to crowdsource innovation, interact with critical suppliers to innovate, and incorporate customer feedback into product development, for example. An IoT ecosystem could enable completely new business models, goods, and service offerings.
Analytics Driven Business Insight
Superior data mining for companies is a significant – and often the most important – competitive differentiator. Digitally native companies like Uber, Amazon, Facebook, and Google optimise their service offerings nearly in real time based on analytics-driven data. For example, Caterpillar, GE, and Bayer are reorganising their operations to create data-driven revenue streams. Two of the world’s major consumer packaged goods firms, Unilever and Procter & Gamble, compete on the analytical capabilities of their marketing teams.
Digital Workforce And Organisation
Technology has changed the nature of work by automating routine tasks, digitising workflows, linking coworkers in virtual teams, and untethering and empowering knowledge workers with personal productivity tools. These skills employ digital technologies and platforms to boost productivity, intellectual property development, and individual and team value contributions. The majority of today’s digital capabilities, including as knowledge management systems, workforce collaboration platforms like Microsoft Teams, Zoom, and Slack, and other forms of communication and engagement, allow workers to access programmes remotely and provision themselves.
5G and IoT
The fifth generation of mobile network technology is known as 5G. 5G’s major benefits are multi-peak data speeds, low latency, improved user experience, better connectivity and availability, and enhanced network bandwidth.
When 5G is combined with edge computing, some intriguing new possibilities emerge. Verizon and Telefonica, for example, will be able to run their 5G networks using IBM’s cloud services.
As a result, AI, drone-assisted inspections, and video inspections will automate regular processes while avoiding network issues.
Software 2.0
Software 2.0 is a system that generates source code from requirements documents automatically. This can be accomplished using Deep Learning (DL), which aids in the development of neural networks for the automation of code drafting.
Data Fabric
The global data fabric market is estimated to reach USD 4.2 billion by 2026, according to MarketsandMarkets.
What is Data Fabric, exactly? Gartner uses a great analogy to define data fabric. Consider the following two scenarios involving the use of a self-driving car:
When the autonomous features are not in use, the driver drives manually.
When the driver loses concentration, the autonomous features take over and make necessary route corrections.
Hyperautomation
Hyper Automation is a project that aims to automate a large number of business and IT processes. Whether it’s through RPA (Robotic Process Automation), low-code/no-code adoption, or AI and machine learning, businesses expect to boost their automation efforts.

